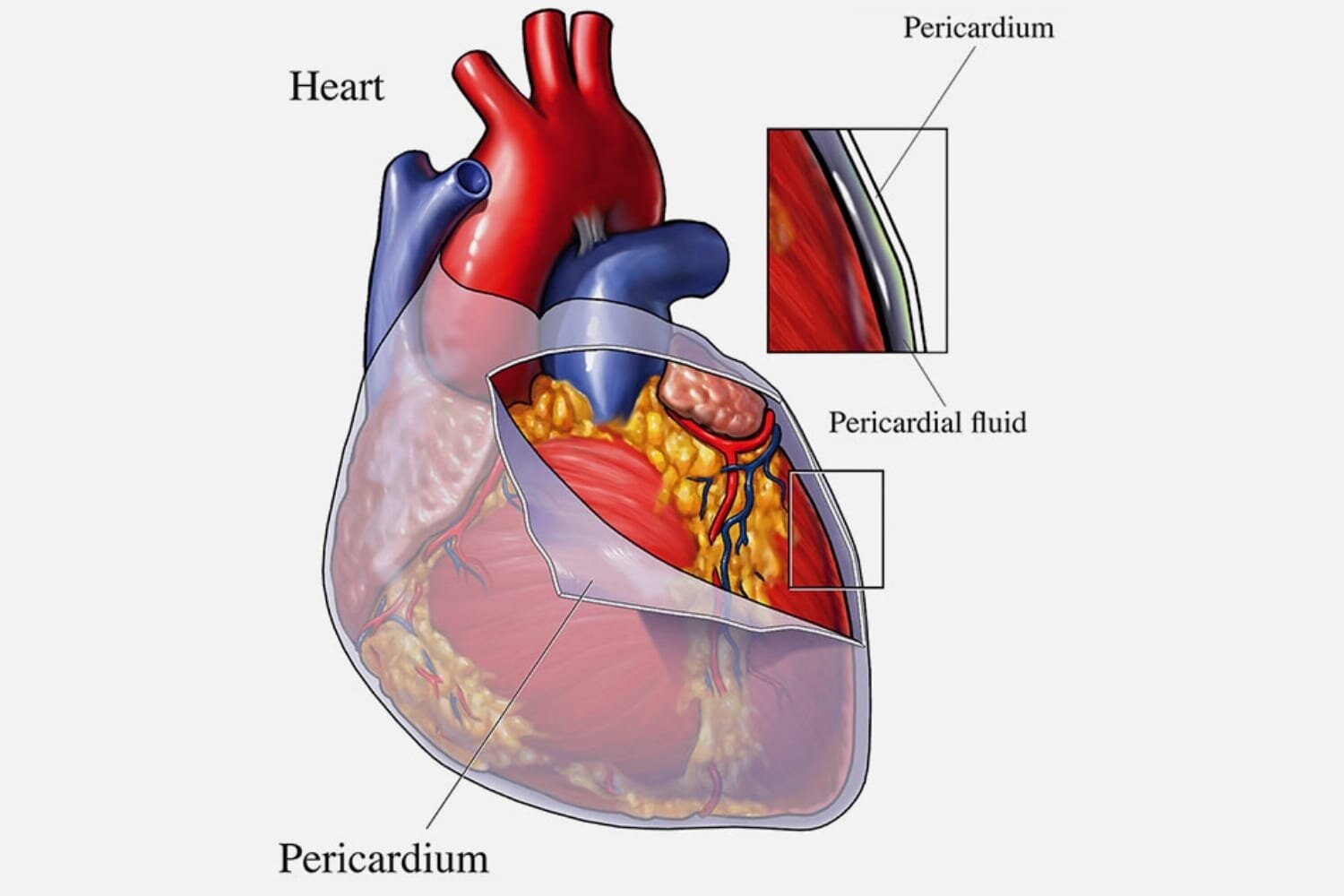
Pericarditis overview
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, two thin, protective layers of a sac-like tissue surrounding the heart, holding it in place and helping it work. Normally a small amount of fluid keeps the layers separate and allows them to move against each other without irritation.
Dr. Leandro Perez reviews the management, causes, signs and symptoms, complications, diagnosis and treatment for pericarditis.
Pericarditis causes
It can often be hard for doctors to decipher what caused the membrane to become inflamed, but some common causes include:
Viral infections
Bacterial infections
Medication side effects
Renal disease
High blood pressure
Illicit drug use
Congestive heart failure
occasionally, the cause is unknown (idiopathic)
Symptoms of pericarditis
Pericarditis can cause severe chest pressure, severe chest pain, pain can be worse with positional changes and deep breaths or coughing. A fever may develop and other infectious constitutional symptoms may be present.
Pericarditis diagnosis
Your doctor will obtain a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination. An electrocardiogram (EKG) and echocardiogram as well as blood and urine tests are typically recommended.
Pericarditis treatment
Treating any underlying infectious disease is critically important. Anti-inflammatory medications are required, occasionally for prolonged periods, especially in recurrent cases.
To request a consultation click below or call (239) 300–0586